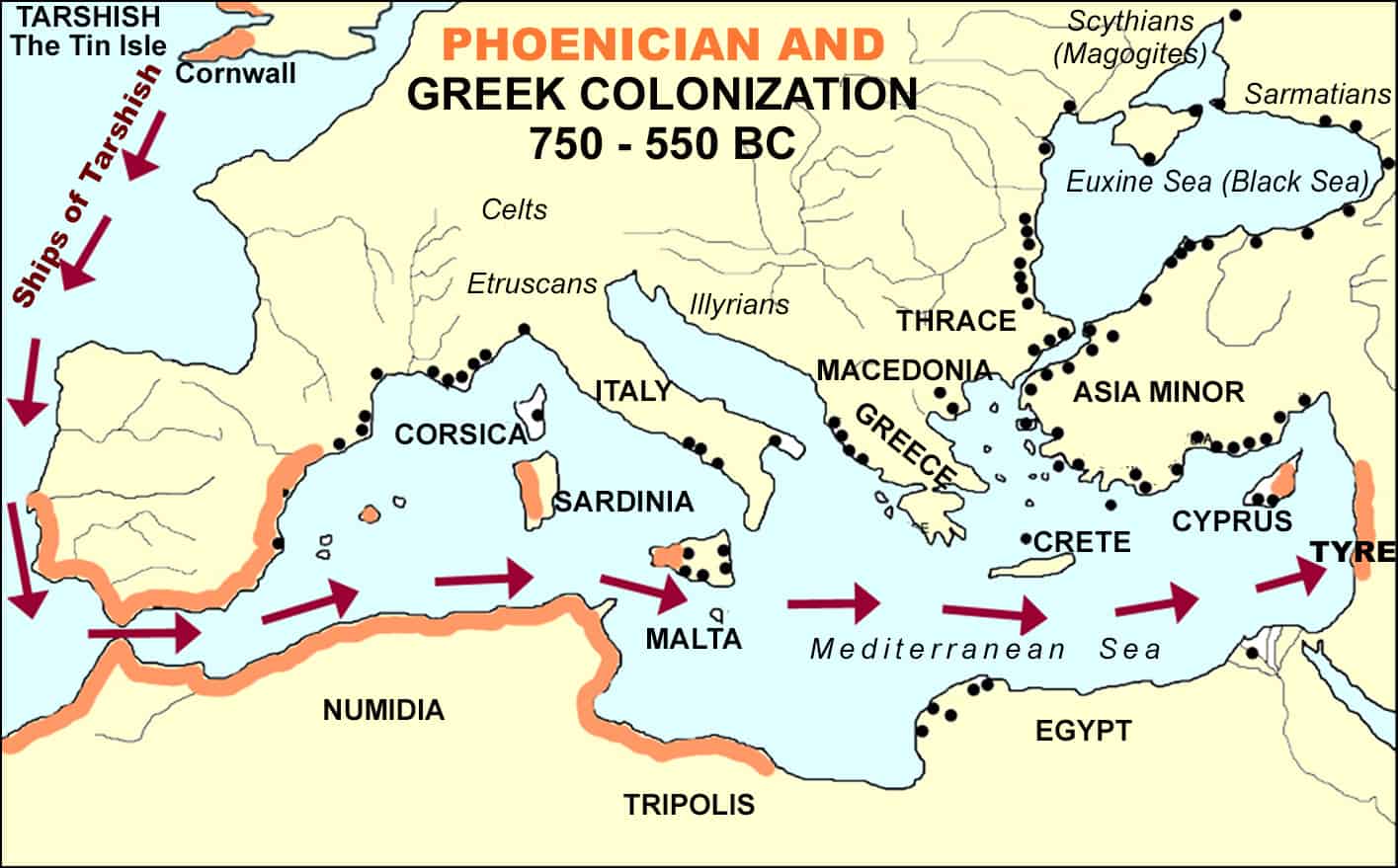
15 Greek And Phoenician Colonies 750 550bc The Herald Of Hope Between 800 and 550 bce, the greek and phoenician civilisations engaged in widespread colonisation across the mediterranean and beyond, driven by economic, political, and demographic factors. Greek territories and colonies (archaic period: 750–550 bc) greek colonies and their metropolitan cities depicted with red labels, while phoenician colonies are depicted with yellow labels (4th century bc).

Greek And Phoenician Colonization Illustration World History Both the ancient greeks and phoenicians extensively colonized vast areas of europe, along the mediterranean and black sea coasts. in doing so, they spread their culture, which strongly influenced the local tribes. Driven by economic necessity and strategic considerations, the greeks established colonies that not only alleviated the pressures on their homeland but also facilitated the spread of greek culture and political ideas across vast territories. Within two hundred years, greek colonies were established in areas that are today southern france, spain, sicily and southern italy, and along north africa and the coast of the black sea. In recent years, however, explaining this dichotomy based on the greeks’ encounter with foreign peoples, or even working with the image of such stereotypes at all, has become a matter of discussion.² the main argument revolves around the question of whether greek ethnicity evolved out of.

Greek And Phoenician Colonies 550 Bc Map Collection Within two hundred years, greek colonies were established in areas that are today southern france, spain, sicily and southern italy, and along north africa and the coast of the black sea. In recent years, however, explaining this dichotomy based on the greeks’ encounter with foreign peoples, or even working with the image of such stereotypes at all, has become a matter of discussion.² the main argument revolves around the question of whether greek ethnicity evolved out of. After colonisation the ancient greek world stretched from libya and southern france to cyprus, asia minor and the crimean peninsula. sailing existing sea routes, the colonists captured land typically occupied by a vulnerable non greek people. Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of archaic greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries bc, across the mediterranean sea and the black sea. Whereas the phoenicians were interested primarily in establishing trading centres and developing new markets, greek colonies were formed above all in response to the constantly increasing population density that threatened to overtax the capacities of cities in the motherland. It is sometimes held by iris, another messenger of the gods (usually hera), or by nike, who in this context serves as the herald of victory. hermes, the god of herdsmen, was also known by the.

Ancient World History Phoenician Colonies After colonisation the ancient greek world stretched from libya and southern france to cyprus, asia minor and the crimean peninsula. sailing existing sea routes, the colonists captured land typically occupied by a vulnerable non greek people. Greek colonisation refers to the expansion of archaic greeks, particularly during the 8th–6th centuries bc, across the mediterranean sea and the black sea. Whereas the phoenicians were interested primarily in establishing trading centres and developing new markets, greek colonies were formed above all in response to the constantly increasing population density that threatened to overtax the capacities of cities in the motherland. It is sometimes held by iris, another messenger of the gods (usually hera), or by nike, who in this context serves as the herald of victory. hermes, the god of herdsmen, was also known by the.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Ancient_colonies2-9f26d3f8f2ff42629e6ce79efafa26a5.jpg)
30 Maps Of Ancient Greece Show How It Became An Empire Whereas the phoenicians were interested primarily in establishing trading centres and developing new markets, greek colonies were formed above all in response to the constantly increasing population density that threatened to overtax the capacities of cities in the motherland. It is sometimes held by iris, another messenger of the gods (usually hera), or by nike, who in this context serves as the herald of victory. hermes, the god of herdsmen, was also known by the.