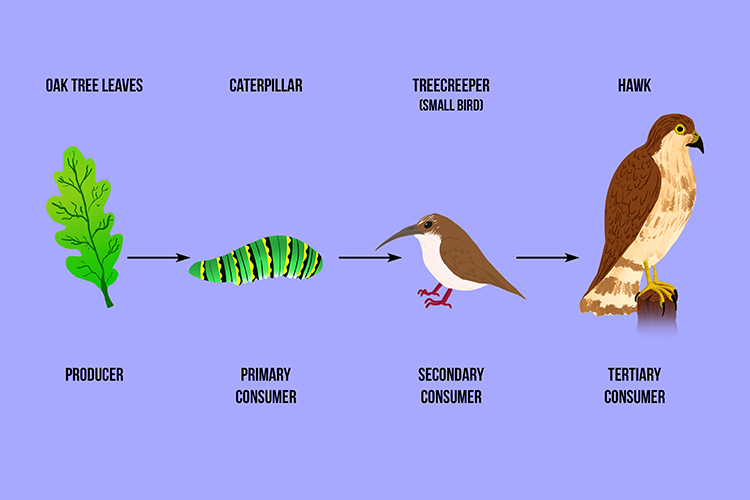
A Tertiary Consumer Eats Secondary Animals In The Food Chain A tertiary consumer is an animal that eats primary and secondary consumers, usually a carnivore or an omnivore. learn about the ecological role of tertiary consumers, such as big cats, sharks, whales and humans, and how they affect the food chain and the ecosystem. Discover what tertiary consumers are, their essential place in food chains, and their impact on ecosystem health.

Food Webs And Energy Ppt Download A tertiary consumer is an organism that obtains the energy it needs from consuming other consumers at different levels, from eating primary consumers or secondary consumers. A tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. it eats both primary and secondary consumers as its main source of food. learn about some examples of tertiary consumers in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and their ecological roles. A tertiary consumer is an organism that primarily obtains its energy by feeding on secondary consumers. this consumer occupies the fourth level of energy transfer in an ecosystem, following producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. Learn about tertiary consumers with green ecologist. here we explain from what tertiary consumers are, their characteristics and examples, to why there are few in ecosystems and.

Tertiary Consumer Biology Simple A tertiary consumer is an organism that primarily obtains its energy by feeding on secondary consumers. this consumer occupies the fourth level of energy transfer in an ecosystem, following producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. Learn about tertiary consumers with green ecologist. here we explain from what tertiary consumers are, their characteristics and examples, to why there are few in ecosystems and. Primary consumers are the second step, and secondary consumers are the third. this makes a tertiary consumer the fourth step in the food chain because they consume secondary consumers for energy. What are 4 tertiary consumers? tertiary consumers are ones that are on the fourth trophic level. some examples of tertiary consumers are sea turtles, sea lions, hawks, and foxes. Tertiary consumers are organisms that occupy the top tier of the food chain, primarily consuming secondary consumers. these animals are typically carnivorous and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by regulating the populations of species they prey upon. In some food chains, this level of consumer is the last link in the chain. often, tertiary and quaternary consumers are considered predators, or even apex predators.

Food Chain For Kids Food Chain And Food Web Primary consumers are the second step, and secondary consumers are the third. this makes a tertiary consumer the fourth step in the food chain because they consume secondary consumers for energy. What are 4 tertiary consumers? tertiary consumers are ones that are on the fourth trophic level. some examples of tertiary consumers are sea turtles, sea lions, hawks, and foxes. Tertiary consumers are organisms that occupy the top tier of the food chain, primarily consuming secondary consumers. these animals are typically carnivorous and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems by regulating the populations of species they prey upon. In some food chains, this level of consumer is the last link in the chain. often, tertiary and quaternary consumers are considered predators, or even apex predators.