
What Is The Difference Between Primary Secondary And Tertiary Consumers Primary consumers serve as the link that transfers energy from plants to the animal kingdom, while secondary consumers act as the next step, transferring that energy further up the food chain. primary and secondary consumers both contribute to the balance and energy flow of ecosystems. Primary consumers are herbivores that eat plants, while secondary consumers are carnivores that eat primary consumers. primary consumers are the first level of consumers in the food chain, whereas secondary consumers follow.

Chapter 3 Page Chapter 4 Page Ppt Download Primary consumers eat plants; secondary consumers eat primary consumers. this simple distinction explains a lot about feeding relationships in nature and how energy travels through ecosystems. Primary consumers are organisms that eat producers or autotrophs, which are typically plants. secondary consumers are organisms that eat primary consumers. in other words, primary consumers are herbivores, while secondary consumers can be either carnivores or omnivores. Primary consumers obtain their food from producers (plants). secondary consumers obtain energy by eating primary consumers (herbivores). example krill eats grass. example small fish eats krill. differentiate between primary and secondary consumers. Primary consumers refer to the organisms that feed on primary producers, and secondary consumers refer to the organisms that feed on primary consumers while tertiary consumers refer to the animals that obtain their nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers.

What Distinguishes Primary And Secondary Consumers Primary consumers obtain their food from producers (plants). secondary consumers obtain energy by eating primary consumers (herbivores). example krill eats grass. example small fish eats krill. differentiate between primary and secondary consumers. Primary consumers refer to the organisms that feed on primary producers, and secondary consumers refer to the organisms that feed on primary consumers while tertiary consumers refer to the animals that obtain their nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. Scientists distinguish between several kinds of consumers. primary consumers make up the second trophic level. they are also called herbivores. they eat primary producers—plants or algae—and nothing else. for example, a grasshopper living in the everglades is a primary consumer. The fundamental difference between primary and secondary consumers lies in their source of energy and position within the food chain, often referred to as trophic levels. Primary consumers are herbivores that feed directly on producers like plants, while secondary consumers are carnivores or omnivores that eat primary consumers. this distinction is essential in understanding food chains and ecosystems. Explore the role of secondary consumers in ecosystems, their types, and examples. learn how they connect primary consumers and top predators in the food chain.
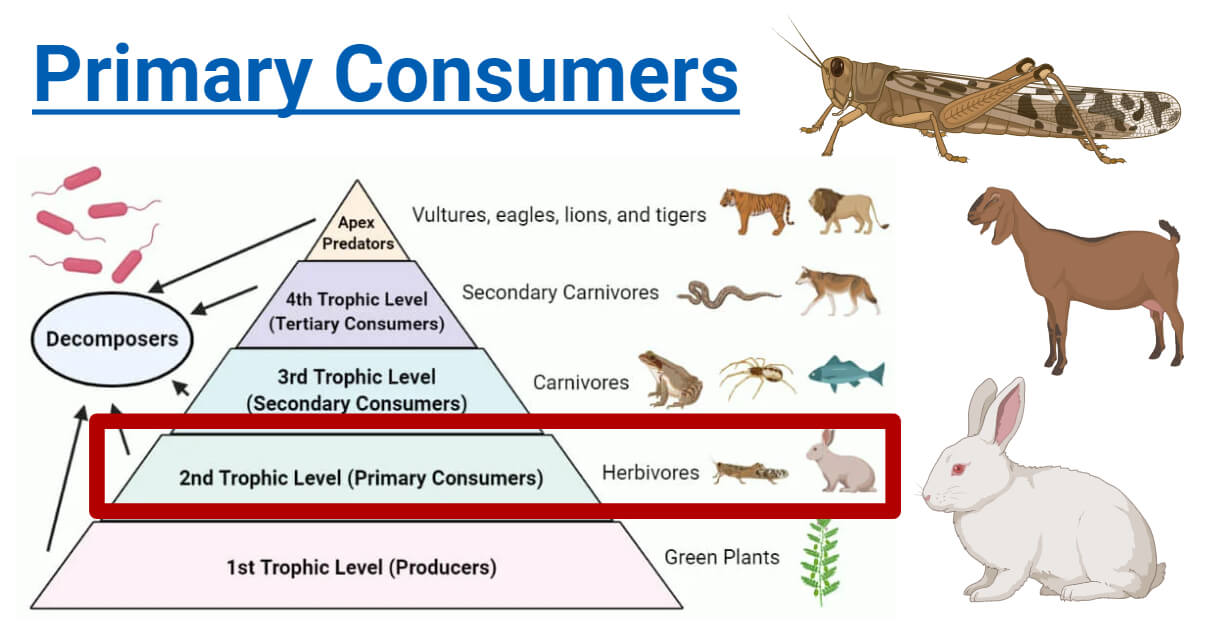
Primary Consumers In Ecosystems Roles Examples Scientists distinguish between several kinds of consumers. primary consumers make up the second trophic level. they are also called herbivores. they eat primary producers—plants or algae—and nothing else. for example, a grasshopper living in the everglades is a primary consumer. The fundamental difference between primary and secondary consumers lies in their source of energy and position within the food chain, often referred to as trophic levels. Primary consumers are herbivores that feed directly on producers like plants, while secondary consumers are carnivores or omnivores that eat primary consumers. this distinction is essential in understanding food chains and ecosystems. Explore the role of secondary consumers in ecosystems, their types, and examples. learn how they connect primary consumers and top predators in the food chain.

What Distinguishes Primary And Secondary Consumers Primary consumers are herbivores that feed directly on producers like plants, while secondary consumers are carnivores or omnivores that eat primary consumers. this distinction is essential in understanding food chains and ecosystems. Explore the role of secondary consumers in ecosystems, their types, and examples. learn how they connect primary consumers and top predators in the food chain.