
Ppt Medication Administration Powerpoint Presentation Id 6303142 8. administering subcutaneous medications.docx free download as word doc (.doc .docx), pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free. Choose the needle length based on the amount of subcutaneous tissue present, based on the patient’s body weight and build. generally, insert the shorter, 3⁄8 inch needle at a 90 degree angle andthe longer, 5⁄8 inch needle at a 45 degree angle.
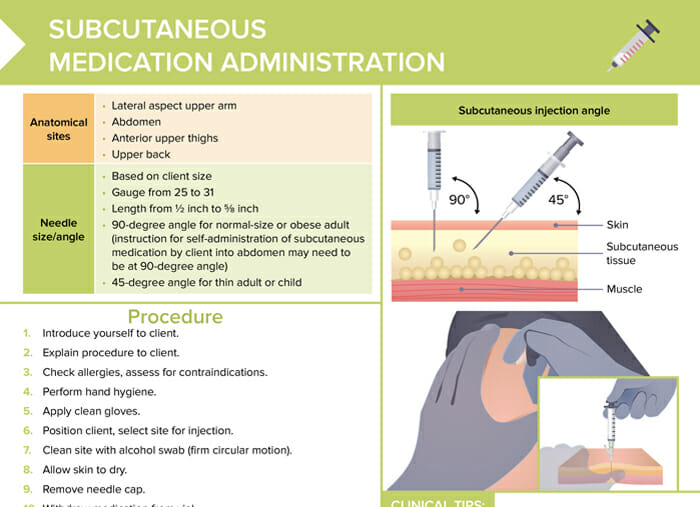
Subcutaneous Injection Technique Learn about subcutaneous infusions: indications, procedures, medications, and potential complications. a guide for healthcare professionals. Examples of common medications administered via subcutaneous injection include insulin and heparin. special considerations for each of these medications are discussed below. This is the second article in a two part route is therefore slower than via the intra as the amount of subcutaneous fat series on injection techniques. part 1 muscular route (see part 1) (dougherty and varies between patients, individual patient covered the intramuscular route. lister, 2015). Administering subcu medications free download as word doc (.doc .docx), pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free.

Administering Medications Through Subcutaneous Route Docx This is the second article in a two part route is therefore slower than via the intra as the amount of subcutaneous fat series on injection techniques. part 1 muscular route (see part 1) (dougherty and varies between patients, individual patient covered the intramuscular route. lister, 2015). Administering subcu medications free download as word doc (.doc .docx), pdf file (.pdf), text file (.txt) or read online for free. Know the actions, special nursing considerations, safe dose ranges, purpose of administration, and adverse effects of the medications to be administered. consider the appropriateness of the medication for this patient. A medication administered into subcutaneous tissues is known as a subcutaneous (sc) injection. sc administration is the preferred route for medications requiring slow, steady absorption (given reduced blood supply to adipose tissue). The document outlines 40 steps for administering a subcutaneous injection, including preparing supplies and medication, identifying the patient, assessing the injection site, administering the injection, and documenting the procedure. Examples of common medications administered via subcutaneous injection include insulin and heparin. special considerations for each of these medications are discussed below.
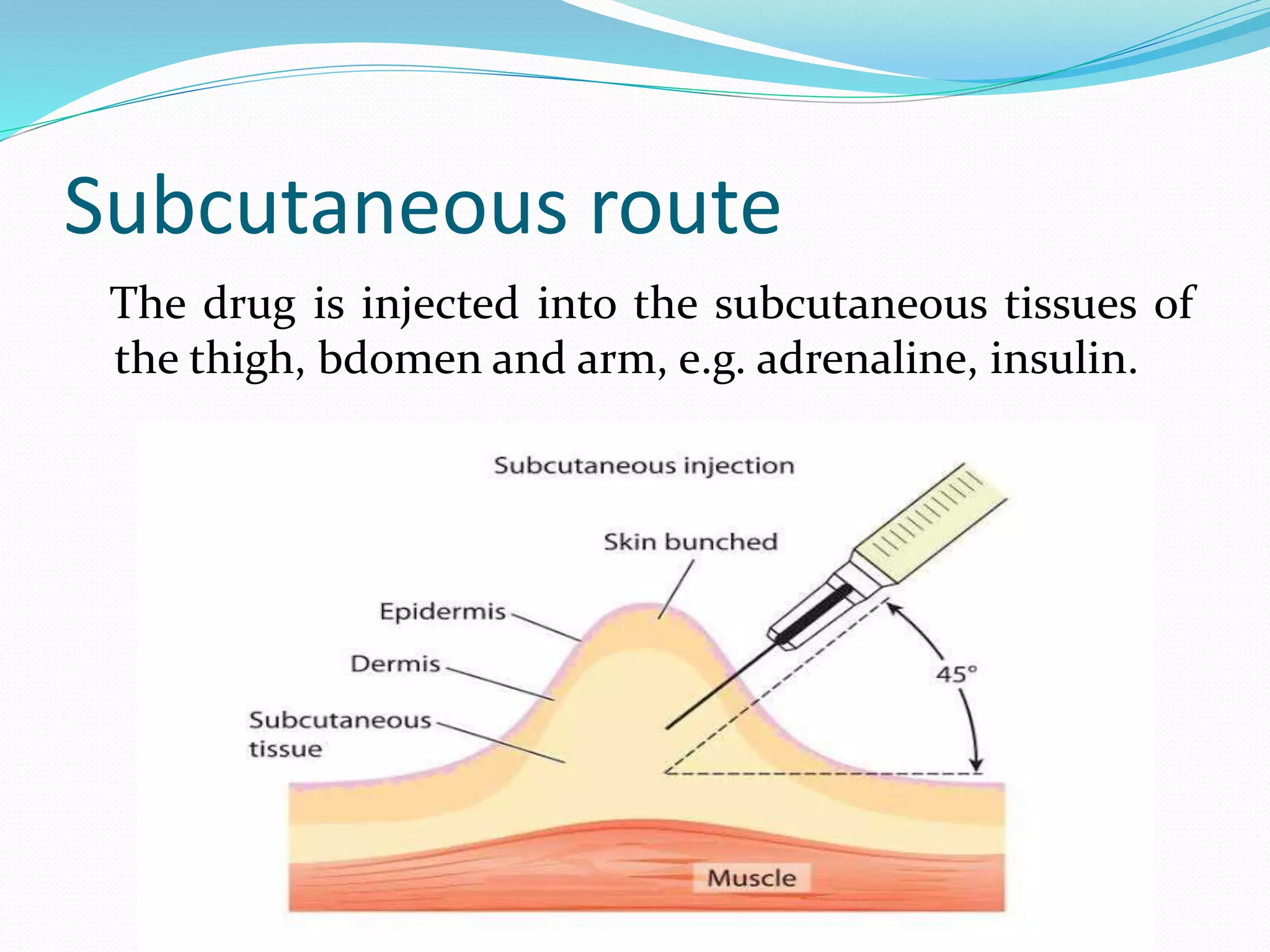
Routes Of Drug Administration Pptx Know the actions, special nursing considerations, safe dose ranges, purpose of administration, and adverse effects of the medications to be administered. consider the appropriateness of the medication for this patient. A medication administered into subcutaneous tissues is known as a subcutaneous (sc) injection. sc administration is the preferred route for medications requiring slow, steady absorption (given reduced blood supply to adipose tissue). The document outlines 40 steps for administering a subcutaneous injection, including preparing supplies and medication, identifying the patient, assessing the injection site, administering the injection, and documenting the procedure. Examples of common medications administered via subcutaneous injection include insulin and heparin. special considerations for each of these medications are discussed below.
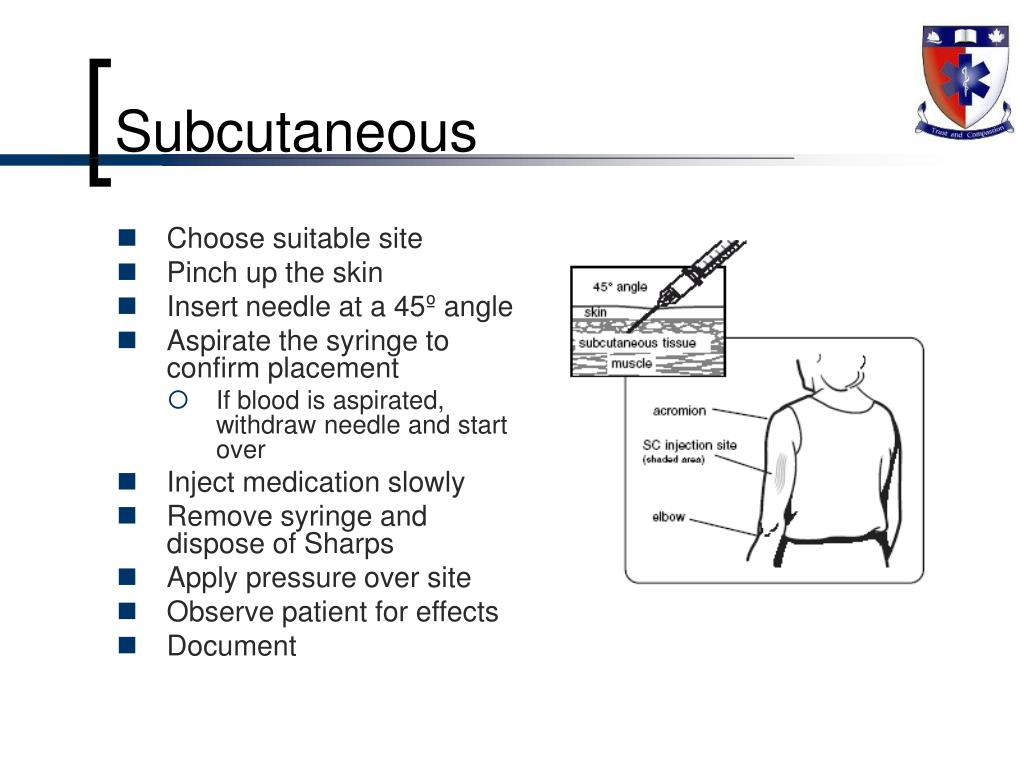
Ppt Medication Routes Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5728223 The document outlines 40 steps for administering a subcutaneous injection, including preparing supplies and medication, identifying the patient, assessing the injection site, administering the injection, and documenting the procedure. Examples of common medications administered via subcutaneous injection include insulin and heparin. special considerations for each of these medications are discussed below.