
FSMA Chinese Postman Problems Student | PDF
FSMA Chinese Postman Problems Student | PDF In graph theory and combinatorial optimization, guan's route problem, the chinese postman problem, postman tour or route inspection problem is to find a shortest closed path or circuit that visits every edge of an (connected) undirected graph at least once. Master the chinese postman problem (cpp) with our detailed guide covering algorithms, complexity analysis, and practical solutions. learn step by step approaches to optimize routing efficiency.

Time-Constrained Chinese Postman Problems
Time-Constrained Chinese Postman Problems Chinese postman problem is a variation of eulerian circuit problem for undirected graphs. an euler circuit is a closed walk that covers every edge once starting and ending position is same. The chinese postman problem was first posed by a chinese mathematician in 1962. it involved trying to calculate how a postman could best choose his route so as to mimise his time. Lecture 9: chinese postman problem • problem: find a minimum length closed path (from and back to the post office), with repeated arcs as necessary, which contains every arc of a given undirected network. It is the problem that the chinese postman faces: he wishes to travel along every road in a city in order to deliver letters, with the least possible distance. the problem is how to find a shortest closed walk of the graph in which each edge is traversed at least once, rather than exactly once.

Chinese Postman Problem | PDF | Vertex (Graph Theory) | Combinatorics
Chinese Postman Problem | PDF | Vertex (Graph Theory) | Combinatorics Lecture 9: chinese postman problem • problem: find a minimum length closed path (from and back to the post office), with repeated arcs as necessary, which contains every arc of a given undirected network. It is the problem that the chinese postman faces: he wishes to travel along every road in a city in order to deliver letters, with the least possible distance. the problem is how to find a shortest closed walk of the graph in which each edge is traversed at least once, rather than exactly once. Learn about the chinese postman problem for your ib maths ai course. find information on key ideas, worked examples and common mistakes. We model this problem using a directed graph. edges and nodes represent streets and intersections, respectively. the length of a street is represented by the weight of the corresponding edge. by using directed edges, it's possible to also account for one way streets etc in the graph. Definition of chinese postman problem, possibly with links to more information and implementations. The problem of finding the optimal eulerization is called the chinese postman problem, a name given by an american in honor of the chinese mathematician mei ko kwan who first studied the problem in 1962 while trying to find optimal delivery routes for postal carriers.
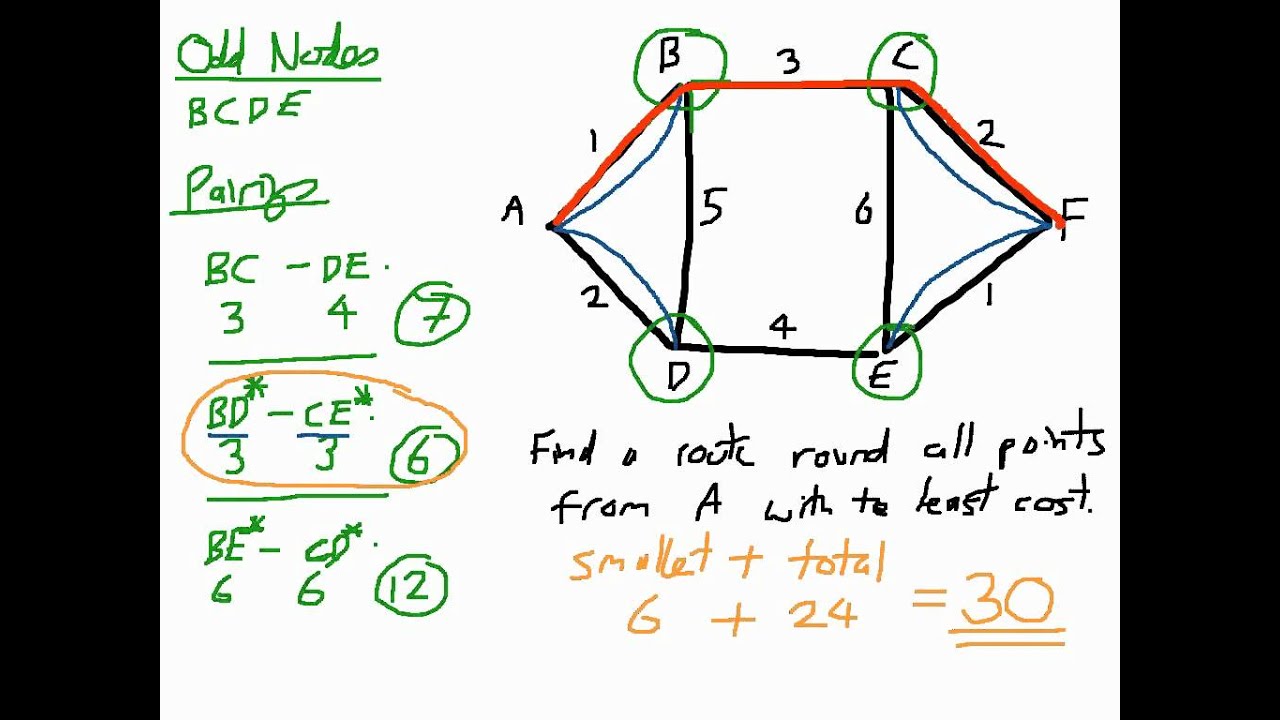
How to Solve Route Inspection Problems - Using the Chinese Postman Algorithm
How to Solve Route Inspection Problems - Using the Chinese Postman Algorithm
Related image with chinese postman problems
Related image with chinese postman problems
About "Chinese Postman Problems"
Our complete collection of chinese postman problems visual content demonstrates the splendor of this remarkable topic. If you're looking for ideas related to chinese postman problems or just appreciating photography, our collection presents something special for every taste. Discover our complete archive of additional chinese postman problems content accessible for your enjoyment. Thank you you for checking out our chinese postman problems collection - we trust you found exactly what you were searching for!













